Describe the Anatomy of a Hair
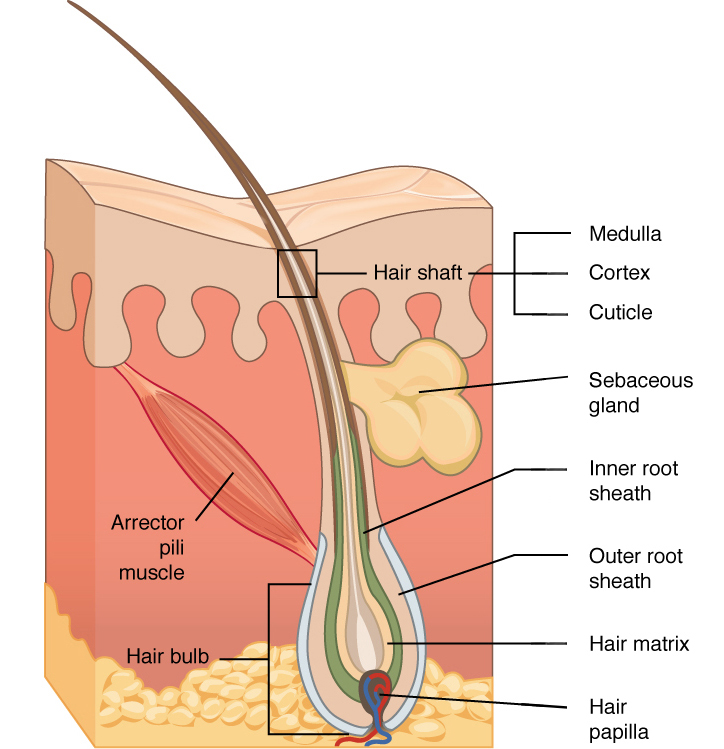
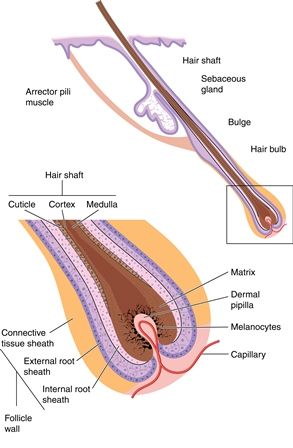
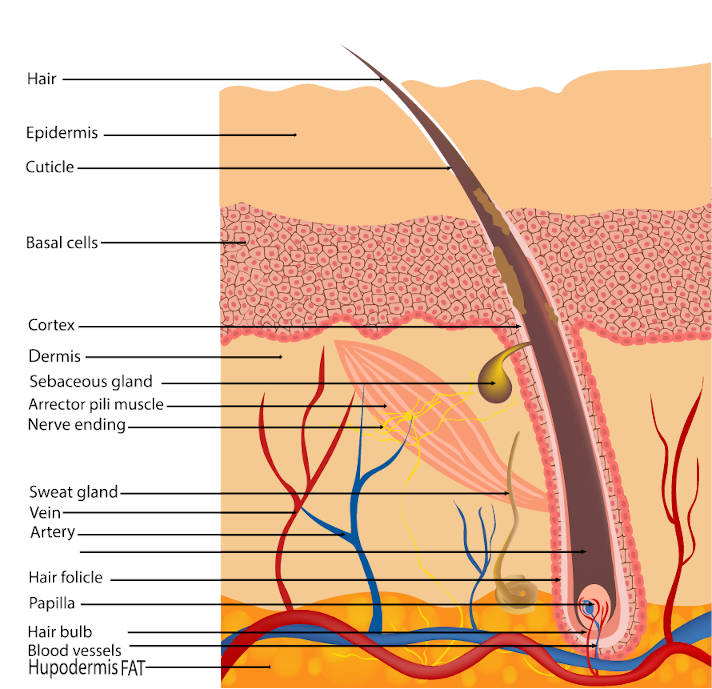
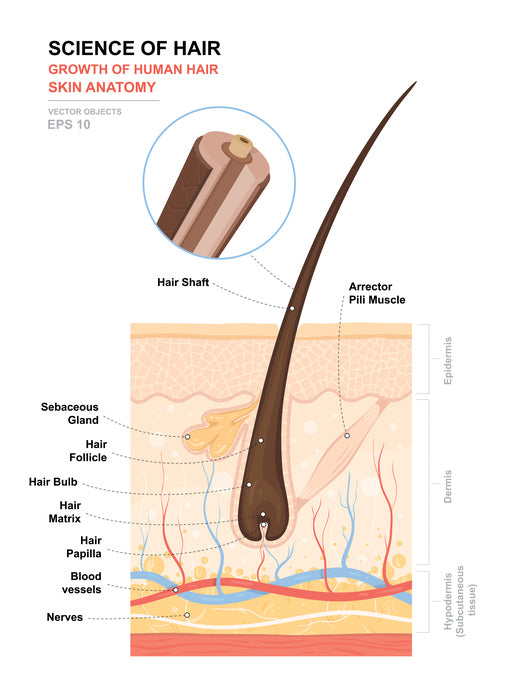
The hair bulb is the lowest expanded extremity of the hair follicle that fits like a cap over the dermal hair papilla enclosing itThe dermal hair papilla is a cluster of mesenchymal cells giving rise to several capillaries which form a capillary loop. The arrector pili muscle APM consists of a small band of smooth muscle that connects the hair follicle to the connective tissue of the basement membrane.

Cross Section Diagram Of The Hair And Scalp Skin Anatomy Integumentary System Skin Facts
Hair is part of the integumentary system.

. Tiny hair cell receptors inside each fluid-filled tube are sensitive to the fluids motion and momentum and this nerve can detect very small changes in orientation to help the body maintain balance. Strands of hair originate from the base of the downward extension of living epithelial cells into the dermis that is called the hair follicle. The ones located in several areas like scalp eyebrows and eyelashes are thicker longer and.
Hair follicle development is related to the interactions between epithelial and mesenchymal cells. The anatomy of the hair bulb includes the components like matrix and the dermal papilla. Then they move those particles toward your nostrils where they can be sneezed out or wiped away.
A hair follicle is a tunnel-shaped structure in the epidermis outer layer of the skin. The skin is the bodys largest organ. The hard bridge at the top of your nose is made of bone.
Your nose anatomy includes. This article describes the personal hygiene and its importance in day to day life. Human hair grows at a rate of 035 mmday and around 100 hairs are shed daily.
Below the surface of the skin is the hair root follicle leading down to the hair bulb. Human hair angiogenesis begins at about ten weeks of gestation and final development results in the mature hair follicle. A bundle of nerves gives sensation to hair Free Edge.
While some have argued that human hair is a vestigial evolutionary remnant in reality human hair serves many psychological and physiological functions. Muscles that pulls hair up. Hair starts growing at the bottom of a.
The hair bulb forms the base of the hair follicle. Anatomy of a follicle. This movement of the hair cells results in the depolarization a change in the balance of electrolytes in the fluid surrounding the cells of the attached nerve fibers and this is how.
The hair follicle begins at the surface of the epidermis. Most of these are tiny colorless vellus hairs. The Growth Cycle.
The individual hairs are always in one of three stages of growth. The hair bulb generates the hair and its inner root sheath. The aim of this chapter is to enhance the knowledge of the complex anatomy and physiology of the hair in a simple manner 2 5.
Hair acts as a dry lubricant in areas that rub such as under the arms and in the groin and serves to disperse pheromones body secretions that are involved in sexual attraction. Hairs vary considerably around the body and in some areas such as the eyelids they do not project beyond the follicles. Graphic with the hair shaft hair root hair follicle hair bulb sebaceous gland arrector pilli and dermal papilla.
Hair inside the skin is generated from the hair follicle or root bulb. Personal hygiene is a healthy way of living. Hair follicles are surrounded by the dermis but the cells are.
A hair follicle anchors each hair into the skin. At the base of the bulb is the papilla small clump of tissue the papilla has a network of capillary blood vessels to supply oxygen energy and amino acids needed for growth. Hair in mammals the characteristic threadlike outgrowths of the outer layer of the skin epidermis that form an animals coat or pelage.
The hair on your scalp grows about a half a millimeter a day. In statum basale growth - part of anatomy of hair. Covering the entire outside of the body it is about 2 mm thick and weighs approximately six pounds.
The part projecting from the surface of the scalp or skin is called shaft. In most other mammals the hair is abundant enough to form a thick coat. The structure and growth cycle of hair is a fascinating process and in this post we explore the key stage of hair development.
The structural or pilosebaceous unit of a hair follicle consists of the hair follicle itself with an attached sebaceous gland and arrector pili muscle. Hair and cilia tiny hairlike structures inside your nose trap dirt and particles. The Anatomy of Hair.
Anatomy and Physiology I. Hair is integral to our body image and can have a profound influence on our self-esteem and self-confidence. The anagen phase is the growth phase of the hair.
Up to 10 cash back 1 Hair Bulb. Anagen catagen and telogen. Many genes play substantial role in this interaction and also in hair follicle cycling 35.
Anatomy What are the parts of your nose. In this section we describe the anatomy of the ear in simple terms. In the hair bulb living cells divide and grow to build the hair shaft.
The part of the hair follicle plays a vital role in the hair growth cycle. The papilla of a hair follicle contains many blood vessels that supply nutrients to nourish the growing hair. The hair cells then brush their stereocilia the tiny hair like projections that reside on top of the cell against a structure called the tectorial membrane.
Most hair spends three to. Anatomy of the Hair. The skin is a vital organ that covers the entire outside of the body forming a protective barrier against pathogens and injuries from the environment.
There is no other part of the human anatomy that. Part of the nail inside your skin. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
For follicles that produce terminal hairs the hair follicle extends into the deep dermis and sometimes even subcutis. Anatomy of the Skin. Past the finger white Nail Root.
Classification of the hair Nearly whole body surface is coated with the hairs except a few areas like palms soles and mucosal regions of lips and external genitalia. Start studying Chp 5 anatomy of hair AP1. The shape of the hair shaft determines whether the hair is curly wavy or straight.
Return to the hair growth information. On adult whales elephants sirenians and rhinoceroses body hair is limited to scattered bristles. Article contains mouth care skin care hair care nail care eye care care of ears care of nose and care of perineum.
The hair bulb is the head of the hair follicle that divides cells to make the hair shaft in a growth cycle and rest. Hair is present in differing degrees on all mammals.
Anatomy Of Hair Imami Hair Restoration
Understanding The Anatomy Of Hair Toppik Blog

I Found This Cool Kahoot Called Describing People Play It And Check Out More Games At Kahoot Com Dictionary For Kids Hair Products Online Hair

Skin Structure Epidermis Dermis Subcutis Subcutaneous Layer Or Hypodermis Biologi Kulit Kesehatan
Hairs Structure Anatomy Functions

Pin By Hoang Long On Spa Integumentary System Skin Anatomy Herbal Hair Oils

Pin By Waleerat Clinic On Waleerat Com Skin Anatomy Epidermis Subcutaneous Tissue

Integumentary System Skin Anatomy Integumentary System Subcutaneous Tissue

Pin By Shereen Mahmoud On Skin Nails Skin Anatomy Skin Structure Anatomy And Physiology

Structure And Composition Of The Hair

Biology The Skin Anatomy Diagram Skin Anatomy Integumentary System Subcutaneous Tissue

Pin By Johndel De Castro On Math Human Body Unit Homeschool Lesson Human Body Worksheets

Cross Section Diagram Of The Hair And Scalp Skin Anatomy Integumentary System Skin Facts

Human Hair Anatomy Hair Follicle Anatomy Ny Hair Loss